New work on the chemical and crystallographic heterogeneities present in a Ni/NiO-YSZ solid oxide fuel cell electrode after re-oxidation
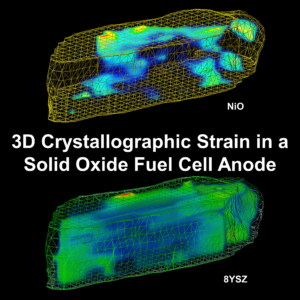 In our latest work, we look with at the chemical and crystallographic heterogeneities present in a Ni/NiO-YSZ solid oxide fuel cell electrode after re-oxidation.
In our latest work, we look with at the chemical and crystallographic heterogeneities present in a Ni/NiO-YSZ solid oxide fuel cell electrode after re-oxidation.
The research was carried out in collaboration with Dr Thomas Heenan from the Electrochemical Innovation Lab (EIL) at UCL Chemical Engineering, UCL Chemistry and ESRF.
The solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode is often composed of nickel (Ni) and yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ). The yttria is added in small quantities (e.g., 8 mol %) to maintain the crystallographic structure throughout the operating temperatures (e.g., room-temperature to >800 °C). The YSZ skeleton provides a constraining structural support that inhibits degradation mechanisms such as Ni agglomeration and thermal expansion miss-match between the anode and electrolyte layers. Within this structure, the Ni is deposited in the oxide form and then reduced during start-up; however, exposure to oxygen (e.g., during gasket failure) readily re-oxidizes the Ni back to NiO, impeding electrochemical performance and introducing complex structural stresses. In this work, we correlate lab-based X-ray computed tomography using zone plate focusing optics, with X-ray synchrotron diffraction computed tomography to explore the crystal structure of a partially re-oxidized Ni/NiO-YSZ electrode. These state-of-the-art techniques expose several novel findings: non-isotropic YSZ lattice distributions; the presence of monoclinic zirconia around the oxidation boundary; and metallic strain complications in the presence of variable yttria content. This work provides evidence that the reduction–oxidation processes may destabilize the YSZ structure, producing monoclinic zirconia and microscopic YSZ strain, which has implications upon the electrode’s mechanical integrity and thus lifetime of the SOFC.
Read the article at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/10/10/941
