X-ray diffraction computed tomography (XRD-CT)
X-ray diffraction computed tomography (XRD-CT) is a pencil beam scanning tomographic technique yielding reconstructed images corresponding to a sample’s cross section. The contrast in these images arises from differences in the signal of the scattered/diffracted X-rays. In conventional X-ray absorption-contrast computed tomography (micro-CT), contrast arises from differences in the density of the sample. For this reason, XRD-CT is able to spatially-resolve chemical species of similar density or low absorption cross section (e.g. C, Li) where conventional micro-CT often fails.
Advantages:
- Non-destructive technique to study objects up to 5 cm in size
- Enables spatially resolved studies on comparatively short time scales (order of minutes)
- Obtained information includes the full chemical map; distribution of chemical species (with submicron resolution) and their physical characteristics (unit cell parameters, crystal size, etc.)
- We are offering a smart collection approach that allows us to choose between spatial and temporal resolution post measurement (interlaced XRD CT)
- XRD-CT can be combined with other imaging modalities like X-ray fluorescence computed tomography (XRF-CT), X-ray absorption fine structure computed tomography (XAFS-CT), pair distribution function computed tomography (PDF-CT) and tomographic Scanning Transmission X-ray Microscopy (STXM).
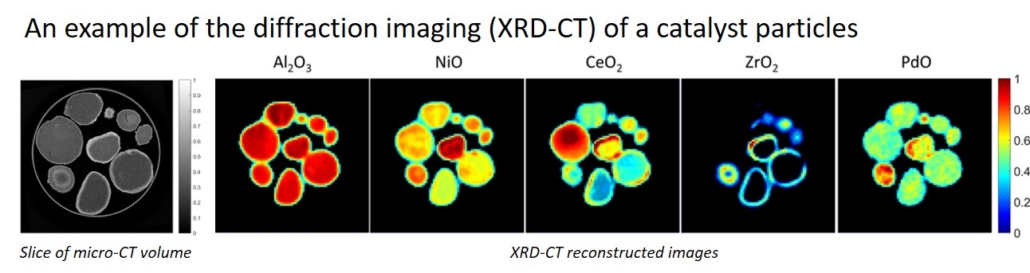
The material used in this study is a complex Ni–Pd/CeO2–ZrO2/Al2O3 catalyst used for methane reforming. For more details see: A. Vamvakeros, S. D. M. Jacques, M. Di Michiel, D. Matras, V. Middselkoop, I. Z. Ismagilov, E. V. Matus, V. V. Kuznetsov, J. Drnec, P. Senecal and A. M. Beale, Nature Communications, 9, 4751, 2018
Further Reading:
5D operando tomographic diffraction imaging of a catalyst bed. A. Vamvakeros, S. D. M. Jacques, M. Di Michiel, D. Matras, V. Middelkoop, I. Z. Ismagilov, E. V. Matus, V. V. Kuznetsov, J. Drnec, P. Senecal & A. M. Beale. (2018). Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 4751
Read a case study using XRD-CT.
If you think that surface X-ray analysis could be helpful for your R&D work do not hesitate to get in touch!
Read about more of the techniques and services we can offer.
